Infection
Aspergillus
Source
Signs in Thoracic Imaging
Journal of Thoracic Imaging 21(1):76-90, March 2006.
Candida

Bronchoscopy showed edematous boggy mucosa and area of darkly pigmented lesions. Cultures showed CANDIDA GLABRATA
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
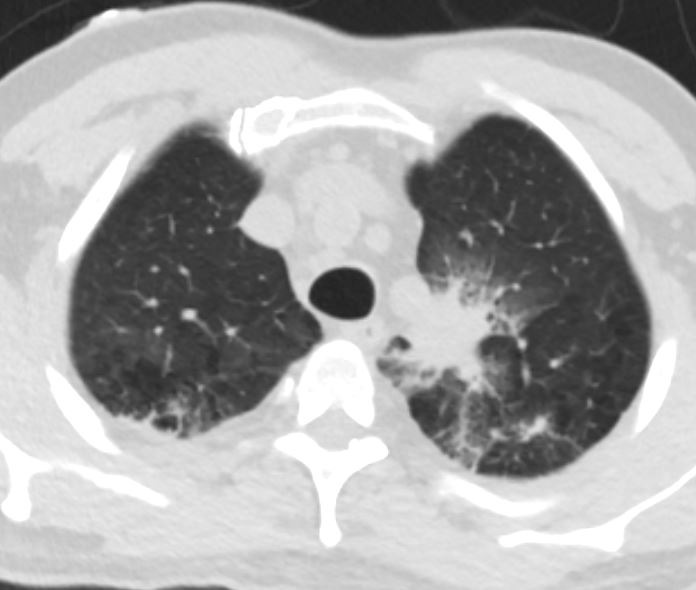
Bronchoscopy showed edematous boggy mucosa and area of darkly pigmented lesions. Cultures showed CANDIDA GLABRATA
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Candida
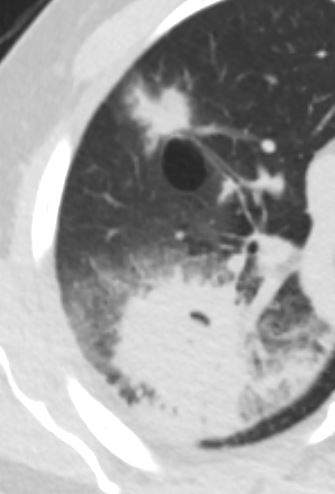
Bronchoscopy showed edematous boggy mucosa and area of darkly pigmented lesions. Cultures showed CANDIDA GLABRATA
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Inflammation
Malignancy
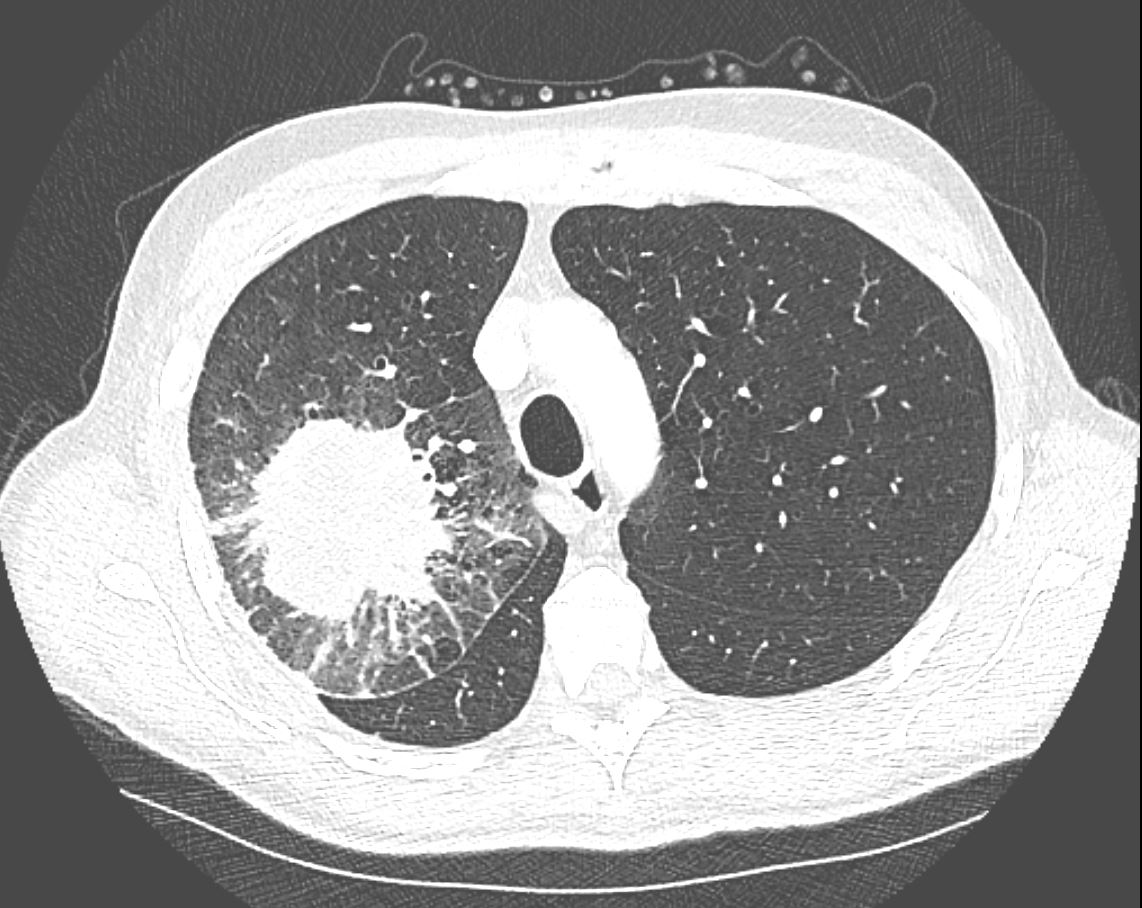
CT in the axial plane demonstrates a large, spiculated mass in the right upper lobe with surrounding halo likely reflecting hemorrhage or lymphatic edema around the mass. In addition, there is evidence of irregular interlobular septal thickening likely reflecting lymphatic invasion and indicating lymphangitis carcinomatosa. There is irregular thickening of the major fissure suggesting involvement.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 135865
Mechanical/Atelectasis
Trauma
Pulmonary Hemorrhage Hematoma Fissural Displacement
Halo Sign – Surrounding Ground Glass Changes
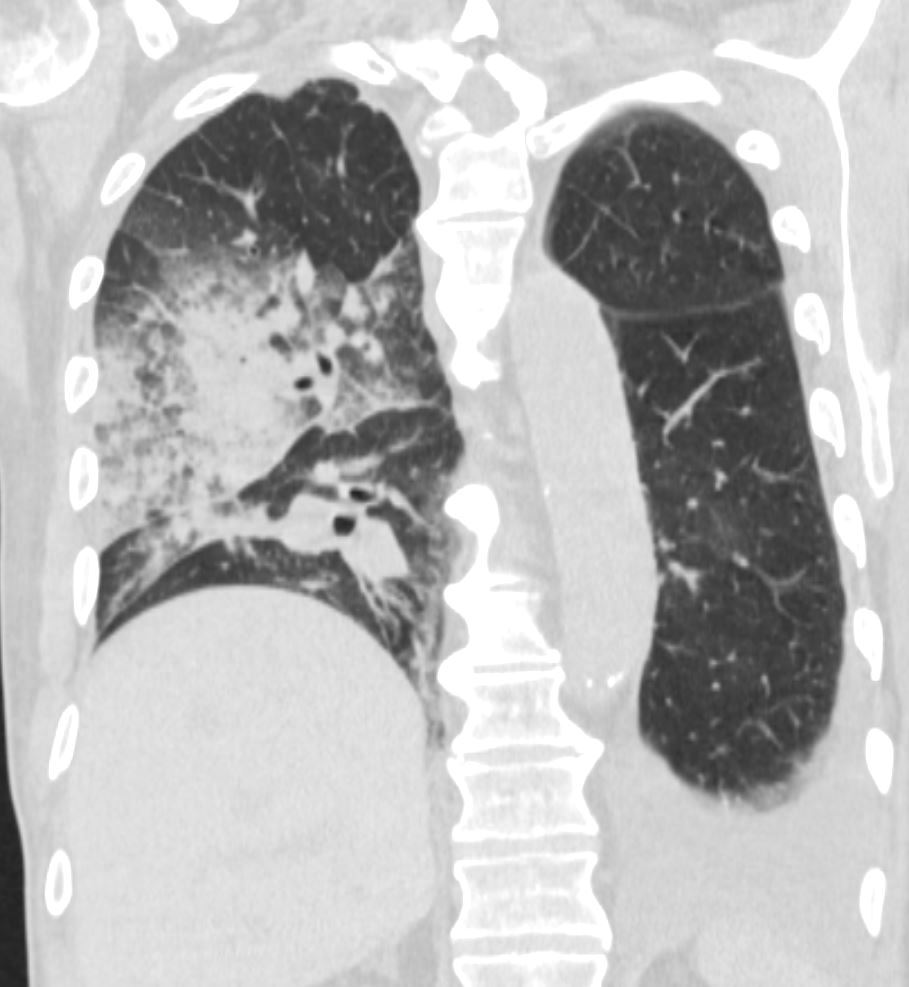
75-year-old man on blood thinners s/p aortic valve replacement, s/p trauma, presents with hemoptysis. He was afebrile and without an elevated white count
Coronal CT of the posterior lung fields shows inferior displacement of the major fissure by a dense right upper lobe consolidation. The mass effect on the major fissure likely results from a hematoma. Lateral to the consolidation there is a combination of ground glass opacity. There is elevation of the right hemidiaphragm. Left sided pleural effusion is present
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 165Lu 135860
Metabolic
Circulatory- Hemorrhage
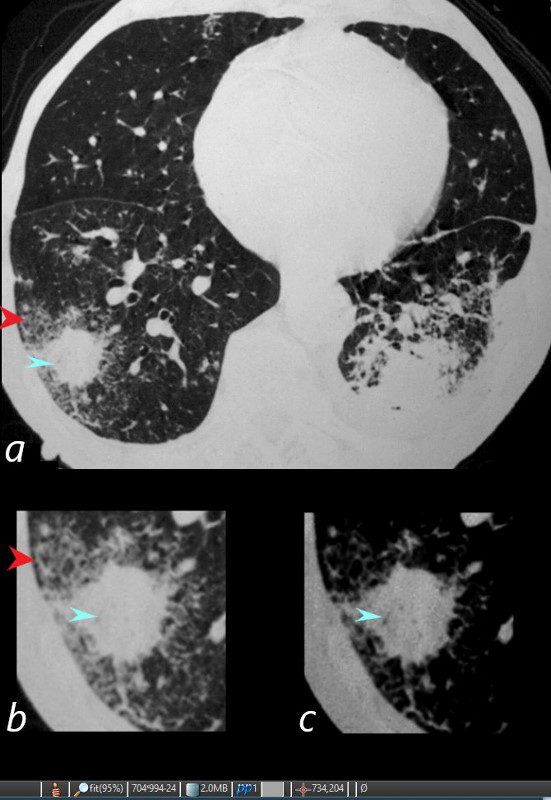
81-year-old male with weight loss, renal failure, and hemoptysis
CT axial view (a) shows a 2 cm solid nodule in the RUL surrounded by A HALO SIGN OF GROUND GLASS CHANGES AND RETICULAR CHANGES (a,b, red arrowheads), indicating surrounding hemorrhage, and subtle air bronchograms (a,b,c, teal arrowheads) best appreciated in c with narrowed windows.
Priscilla Slanetz MPH MD
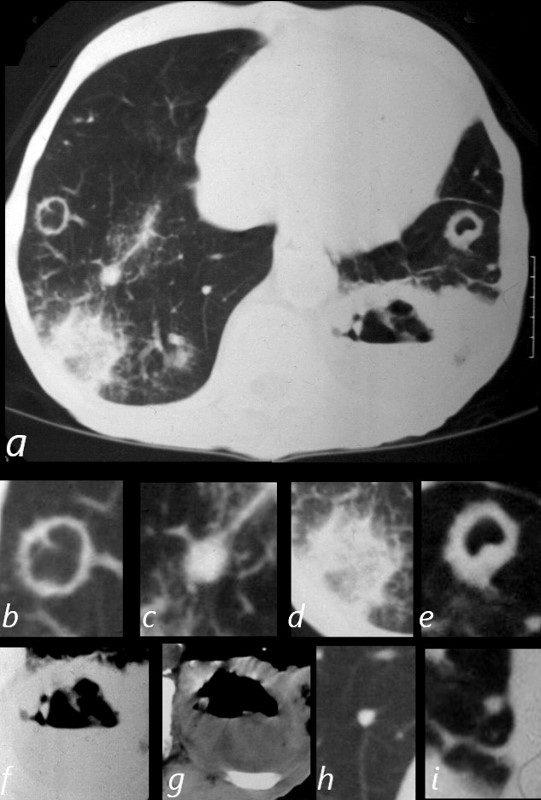
81-year-old male with weight loss, renal failure, and hemoptysis
CT axial view (a) shows cavitating masses in the upper lobes bilaterally magnified (b and e). In addition there is a large necrotic mass with an air fluid level in the left lower lobe (a), magnified ( f and g). A mass with a halo sign noted in the RLL is magnified in d, and scattered bilateral smaller nodules are magnified (c and h) in the RLL and in (i) in the LLL .
Priscilla Slanetz MPH MD
Immune
Immune Deficiency CLL Likely Infection
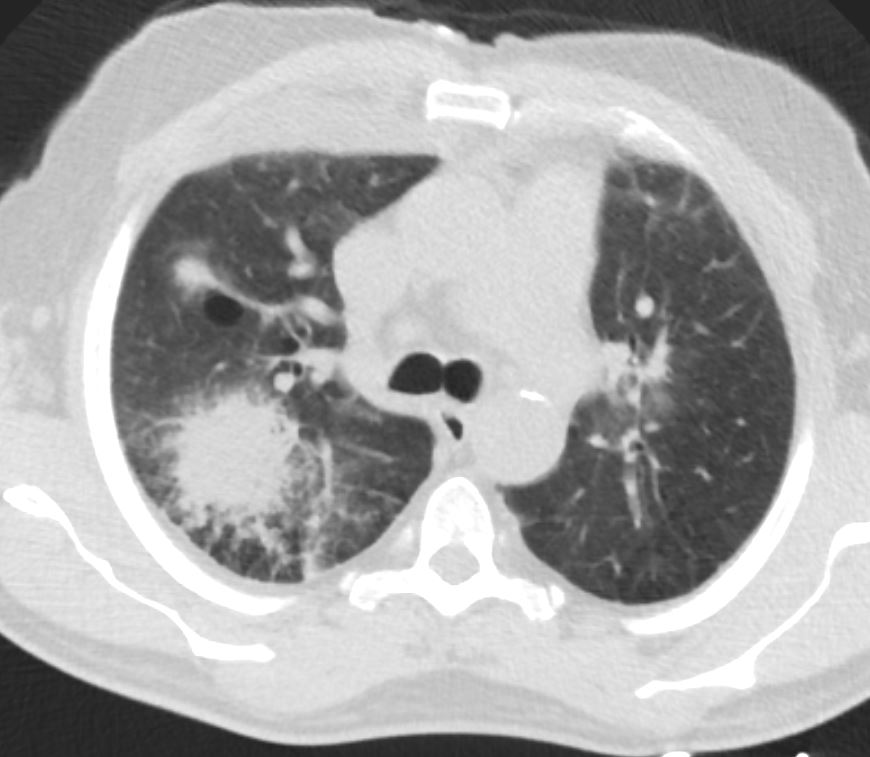
fever and chills 3 days later IR guided CT biopsy of the right upper lobe lesion
progression of disease
neg for AFB
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
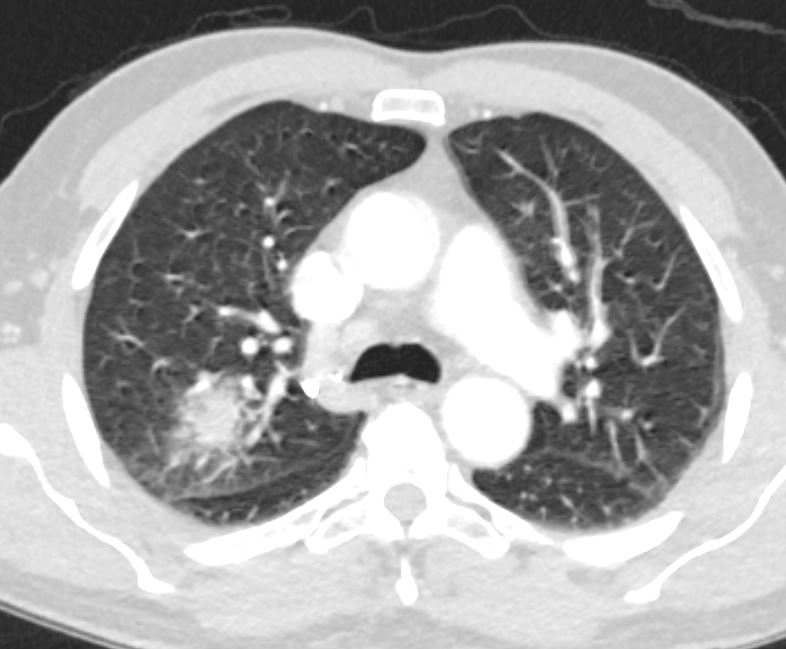
fever and chills neutropenia
CT
new
superior segment of the RUL and RML and
spiculated lesion in the left apex
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
Infiltrative Idiopathic Iatrogenic Idiopathic
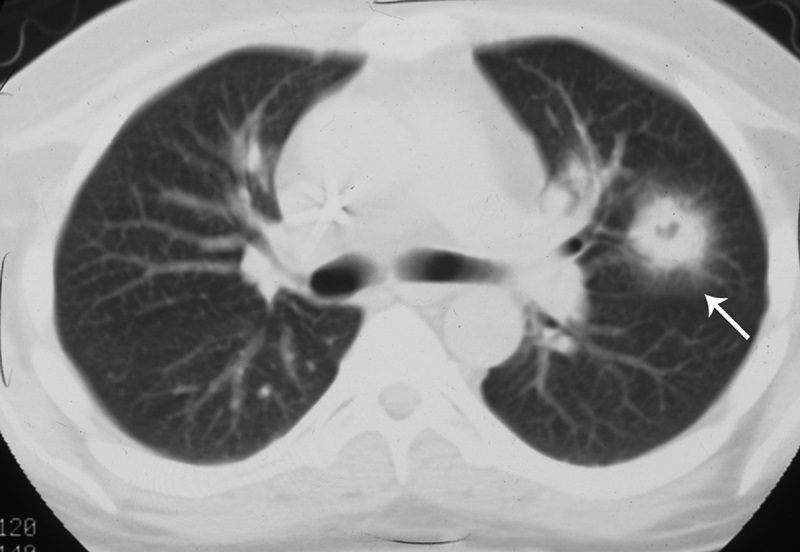
The CT halo sign appears as a zone of ground-glass attenuation around a nodule or mass (Fig. 7) on computed tomographic (CT) images.2–4,6,28 In febrile neutropenic patients, the sign suggests angioinvasive fungal infection, which is associated with a high mortality rate in the immunocompromised host.2–4 The zone of attenuation represents alveolar hemorrhage,2,4,6,28 whereas the nodules represent areas of infarction and necrosis caused by thrombosis of small to medium sized vessels.2–4,6,28,29 Other infectious causes include candidiasis, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, and coccidioidomycosis.30 The CT halo sign may also be caused by non-infectious causes, such as Wegener granulomatosis, metastatic angiosarcoma, Kaposi sarcoma, and brochioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC).29,30 Due to the lepidic growth pattern of BAC, where the tumor cells spread along the alveolar walls, the typical ground glass halo visualized with the sign results.29
