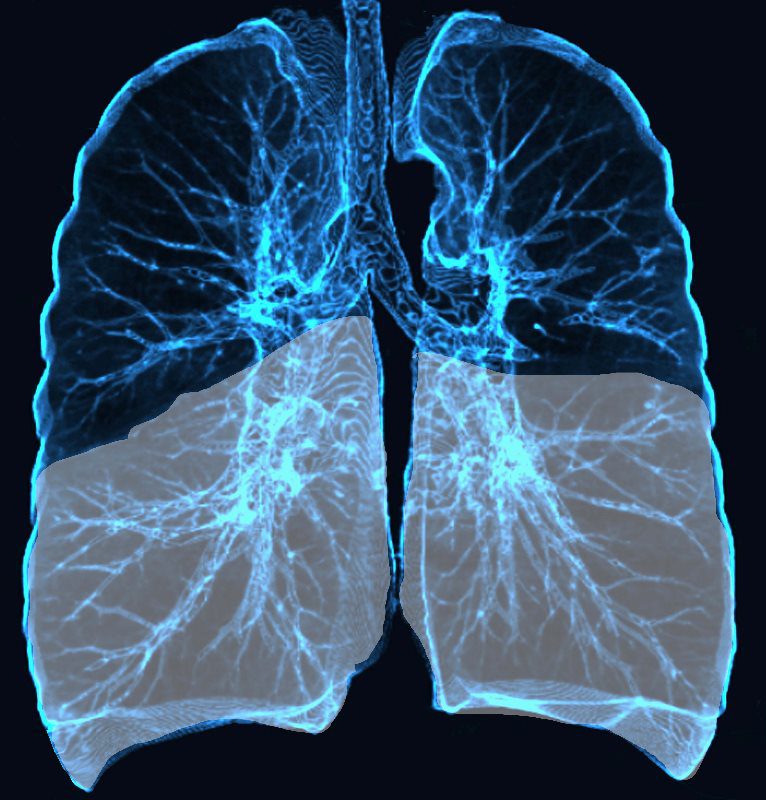
Lower Lobe distribution
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net lungs-0771
aka alveolar macrophage pneumonia
a less angr brother to RB ILD
- Inflammatory
- pigmented intra-alveolar macrophages and giant sells in the alveioli
- Cause
- Mostly smokers
- 10-40% are non smokers
- inhalational toxic
- druga
- viral illness
- autoimmune diseases
- 10-40% are non smokers
- Mostly smokers
- results
- Structural
- Path
- alveoli
- architecture maintained
- macrophages
- uniform diffuse
- Interstitium
- mild chronic inflammation
- alveoli
- CXR
- usually normal
- CT
- widespread
- patchy ground glass
- diffuse less common
- lower lobes (70%)
- bilateral
- relatively symmetrical
- peripheral (60%)
- honeycomb can happen
- Path
- Functional
- LFT mild impairment
- Structural
Buzz
- DIP
- aberrances
- DIP imagine somebody dipping a rag of into cigarette smoke and dabbing it in the lower lung zones smoke
- aberrances
Lungs
- Desquamative –
- squams = misnomer
- infiltrates represent alveolar filling with pigmented macrophages. alveoli
interstitial mucosa/submucosa vessels
pneumonia = “inflammation of the lungs,”
desquamate – fill the alveoli
Small Airways
Inflammation
Secondary Lobule
Alveoli
Inhalation – Lower Lobes
Smokers but
- Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia (DIP) is a rare form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP).
- Cause
- Smokers
- also related to marijuana smoke inhalation,
- infections such as HIV,
- toxins, or
- occupational exposure (eg, to asbestos)
- Smokers
- Results in
- infiltrates represent alveolar filling with pigmented macrophages. alveoli
- Diagnosis
- Clinical
- Cougn Dyspnea
- DX difficult on
- clinical and radiological features alone
- requires a (surgical) lung biopsy
- Imaging
- bilateral ground-glass opacities with
- lower lobe predominance (92%).
- irregular reticulation,
- traction bronchiectasis and
- cysts.
- sometimes
- ground-glass opacities
- architectural distortion,
- traction bronchiectasis and
- honeycombing.
- Clinical
- Path
- pigmented macrophages within
- most of the distal airspace of the lung
- Histologically,
- DIP is similar to RB-ILD,
- DIP and RB-ILD are a spectrum
- differing in compartments involved
- DIP not bronchiolocentric.
- hyperplasia of the alveolar type II cells
- distribution pattern more homogeneous a
- mild peribronchial fibrosis
- DIP is similar to RB-ILD,
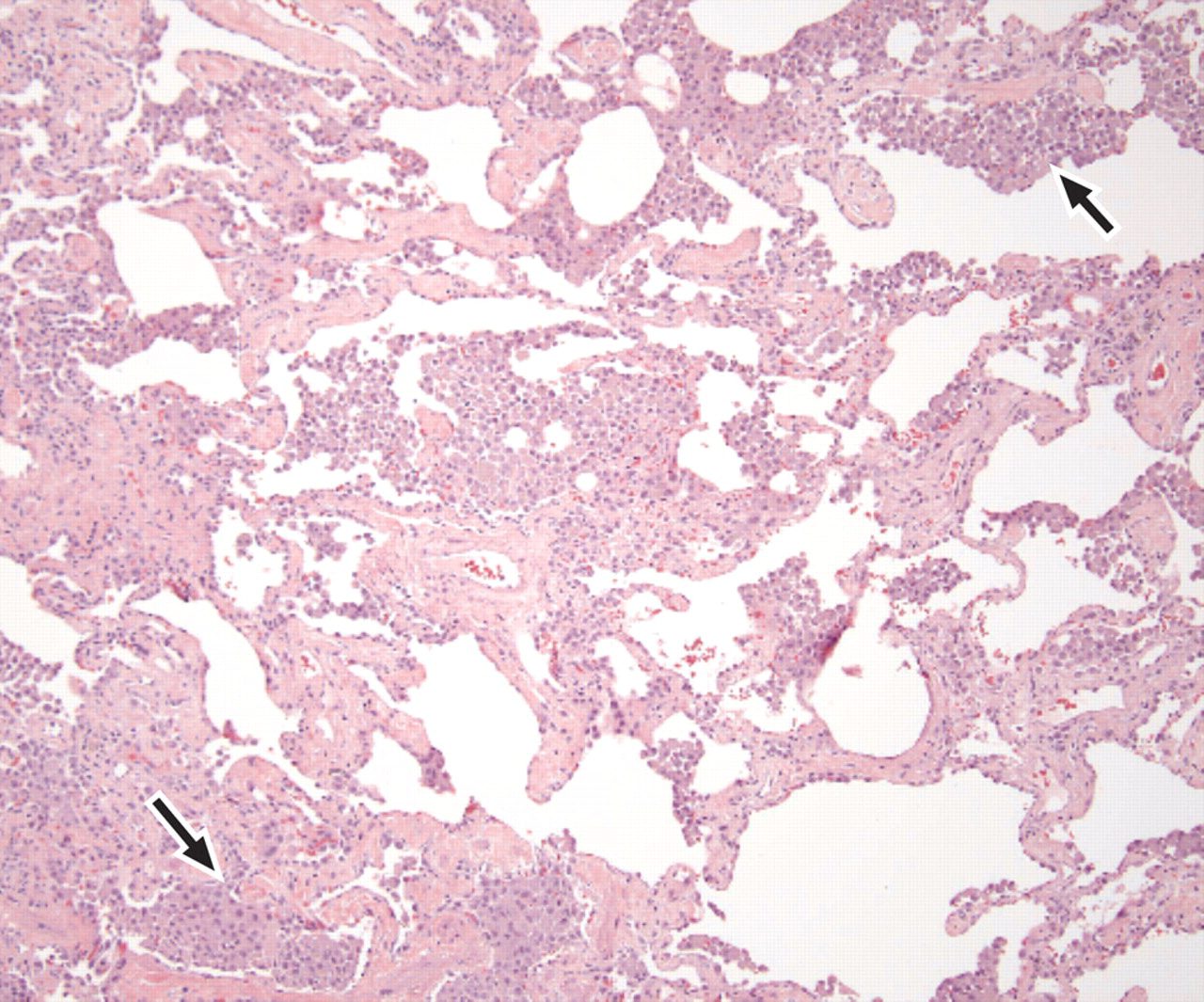
Anil K Smoking related ILD Radiographics

Noted are elevated numbers of macrophages within the alveoli of the lung. The alveolar macrophages have a characteristic light brown pigmentation and accumulate in the alveolar lumen and septa regions of the lower lobes of the lungs. The typical effects of the macrophage accumulation are inflammation and later fibrosis with stiffness of the lung
Courtesy Wiki
web lungs 436

Hellemons M etal Eur Respir Rev 2020; 29: 190181. – September 30, 2020
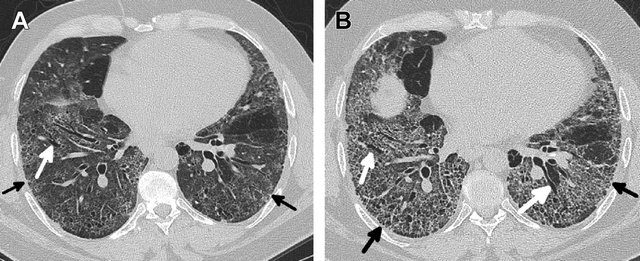
Kligerman S et al Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of Smoking-Related Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease 2016
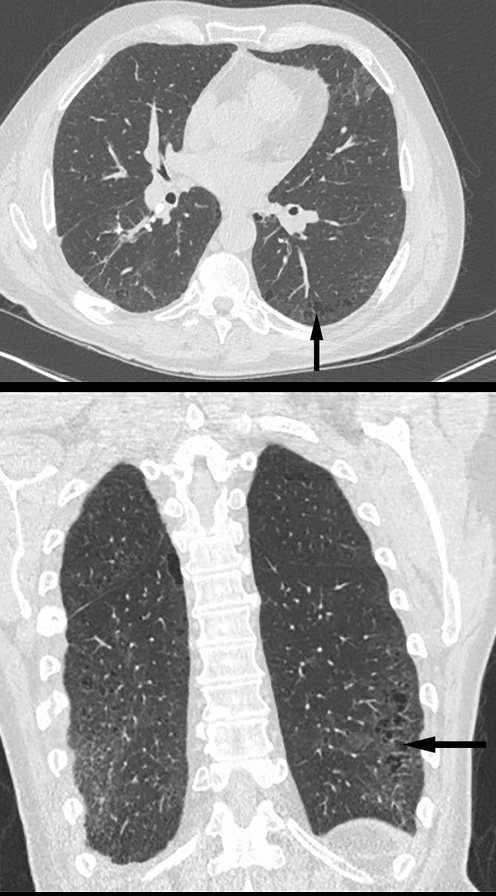
Parekh, M et al Review of the Chest CT Differential Diagnosis of Ground-Glass Opacities in the COVID Era Radiology Vol. 297, No. 3 July 2020
Radiology Buzz
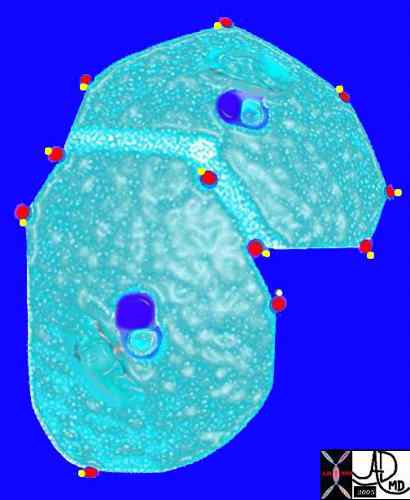
The arteriole and bronchiole lie in the center of the lobule.
Pulmonary venules (red) and lymphatics (yellow). lie in the periphery of the lobule
42440b03
Davidoff Art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
References and Links
Attili, A.K etal Smoking-related Interstitial Lung Disease: Radiologic-Clinical-Pathologic Correlation RadioGraphics Vol. 28, No. 5
Gupta et al Diffuse Cystic Lung Disease: Part I American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 191(12) April 2015
-
TCV
- TCV
-
Videos
-
- Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)
- Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP)
- Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- Idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (PPFE)
