Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net

BAL yielded Mycobacterium Kansasii
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
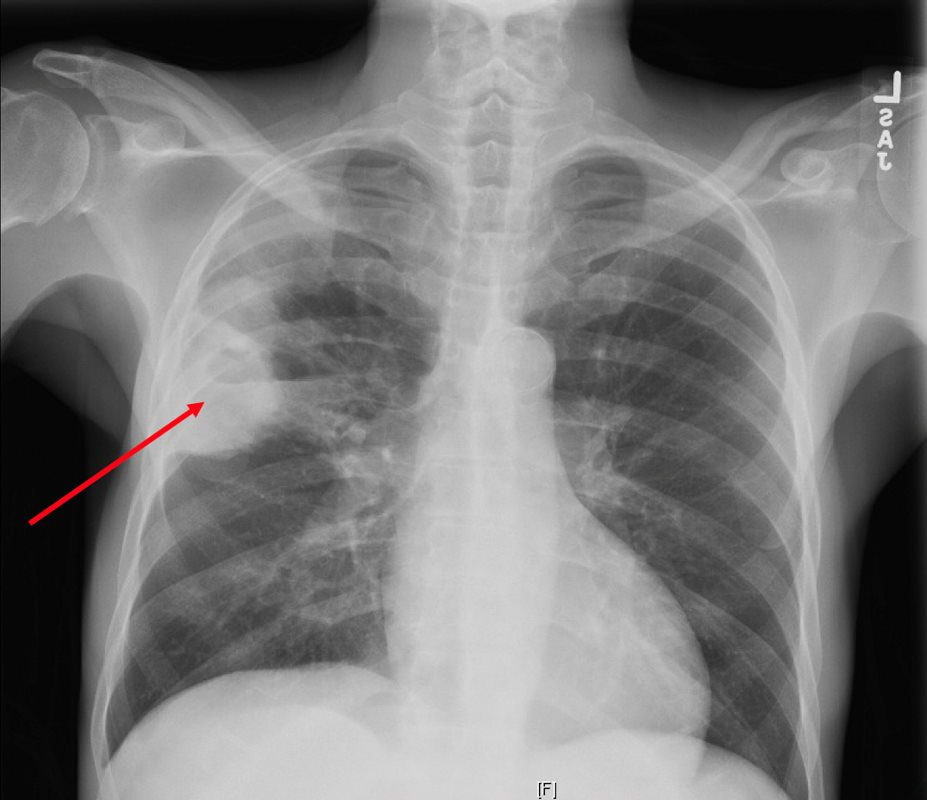
CXR reveals a dense consolidation in the right upper lobe (red arrow) with questionable air-fluid level. No pneumothorax. No pleural effusions. Differential includes right upper lobe pneumonia or tuberculosis. CT is recommended for further evaluation if there is concern for a cavity.
Courtesy Joseph Cannella,
Dr. Christina LeBedis, MD, MS
Courtesy Joseph Cannella,
Dr. Christina LeBedis, MD, MS
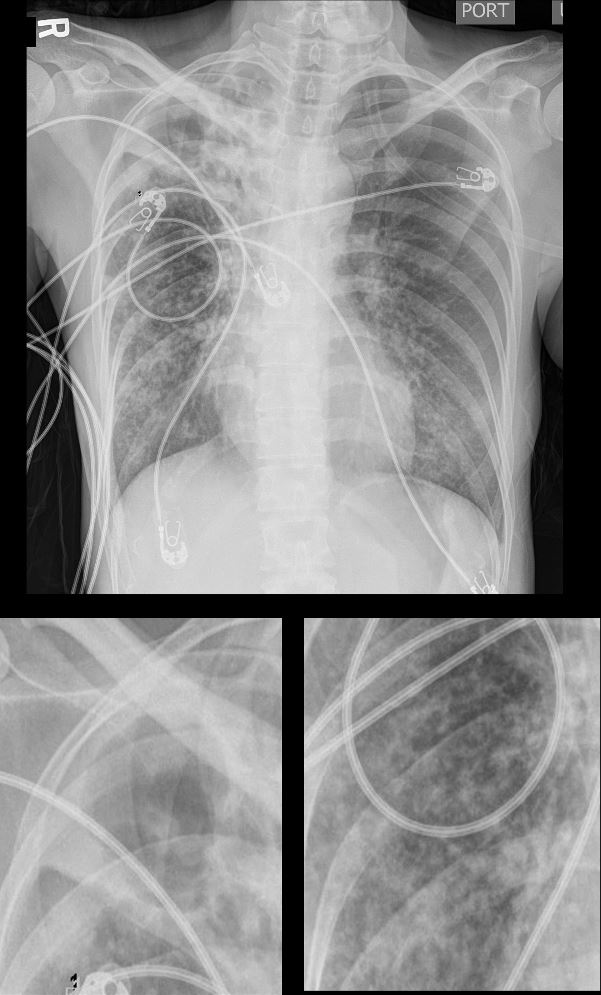
39-year-old immigrant Vietnamese male presents night sweats fever and cough
CXR shows a cavitating lesion in the apex of the right lung (magnified lower image, right) associated with an ipsilateral micronodular pattern (magnified lower image, left)
Although the right lung has the appearance of a “miliary” pattern, this term is usually referred to the hematogenous spread of the disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 131708cL
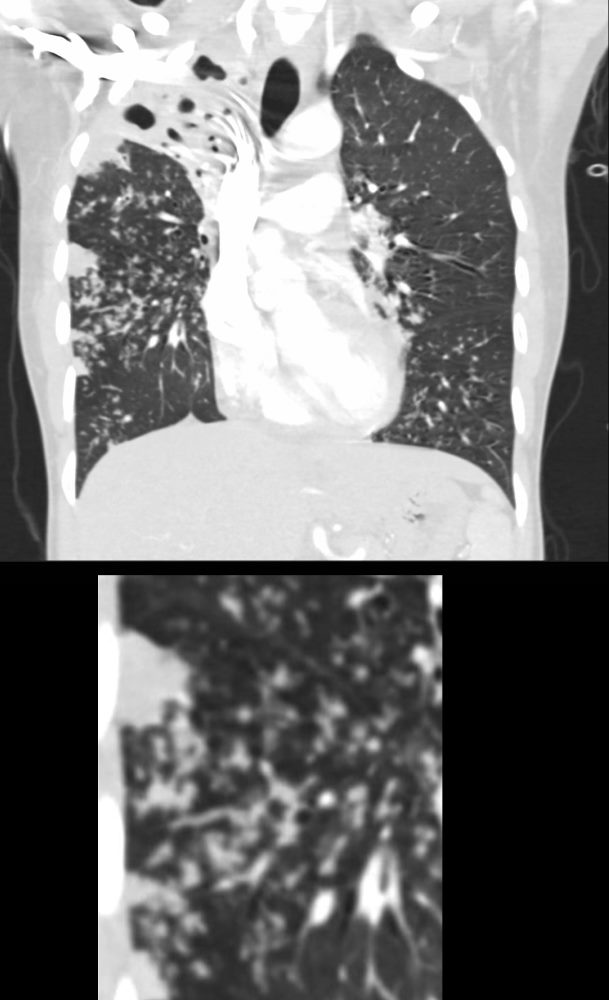
39-year-old immigrant Vietnamese male presents night sweats, fever, and cough. CT in the coronal plane of the chest shows a large cavitating lesion in the right upper lobe, with innumerable micronodules dominantly in the right midlung field, and to lesser extent in the right upper lung field. Some micronodules are probably present in the left lower lobe as well. Close to the largest subsegmental consolidation there is a bronchus which shows thickening of its wall.
Although it has the appearance has a “miliary” pattern, this term is usually referred to the hematogenous spread of the disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135786c
006Lu
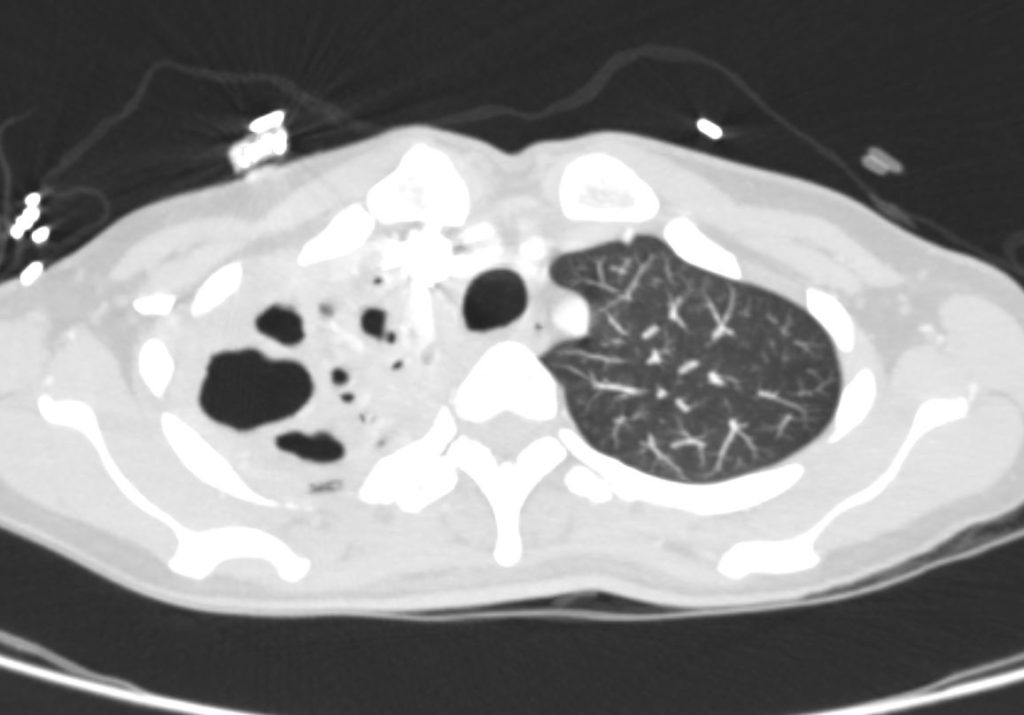
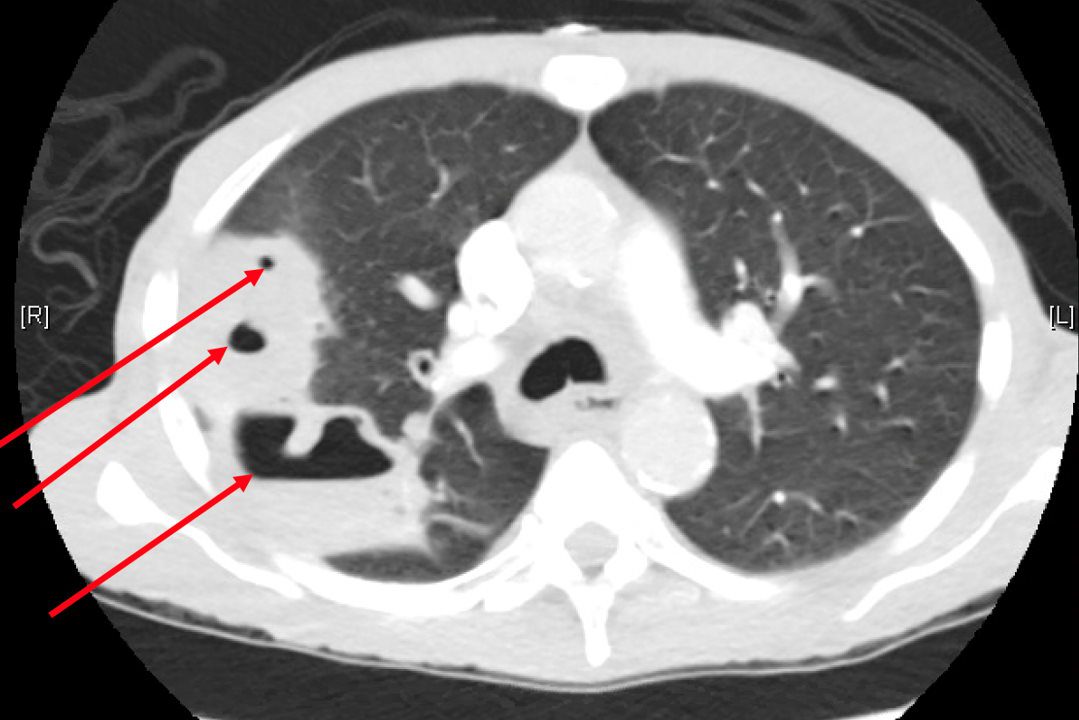
39-year-old immigrant Vietnamese male presents night sweats fever and cough. CT in the axial plane of the chest shows a large cavitating lesion in the right upper apex.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonvein.net 135787 006Lu 006Lu
-
-

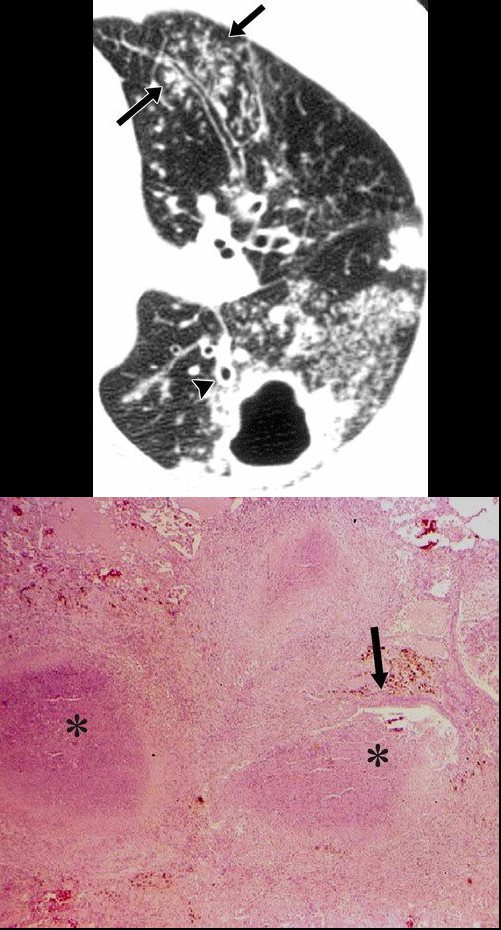
Postprimary active tuberculosis in a 34-year-old man with weight loss and a chronic cough. (a) High-resolution CT scan of the left lung shows a thick-walled cavity and multiple peripheral small nodules and branching linear structures (arrows). Note the thickening of the bronchial walls (arrowhead). (b) Photomicrograph (original magnification, ×400; hematoxylin-eosin stain) shows impacted caseous material (*) in small peripheral airways (arrow).
Rossi, SE et al Tree-in-Bud Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs: Radiologic-Pathologic Overview RadioGraphics Vol. 25, No. 3 2005
-
-
TCV